- 首页
- 关于我们
-
产品中心
- 光片显微镜系列
- LS-COMPACT光片显微镜 LS18平铺光片显微镜 锘海组织透明化底透台 透明度检测仪 组织透明化染色仪 高频震动切片机 活体循环系统 AMIRA三维视图和分析软件 高速固态硬盘
- 透明化试剂盒系列
- 组织透明化试剂盒(亲水型) 组织膨胀试剂盒 胚胎透明化试剂盒 增强型组织透明化试剂盒 细胞膨胀试剂盒 皮肤透明化试剂盒 组织切片透明&膨胀试剂盒(试用装) 骨组织透明化试剂盒 上皮或结缔类组织透明化试剂盒 非固定形态类软组织透明化试剂盒 肿瘤或致密组织透明化试剂盒 颅骨-脑组织透明化试剂盒 植物透明化试剂盒 活体颅骨透明化试剂盒 整鼠透明化试剂盒 Lectin血管标记物 PBS缓冲液 4%多聚甲醛固定液(PFA)
- 组织透明化及成像服务
- 单细胞空间多组学与高通量蛋白质组学科研检测服务 一站式科研服务——组织透明化、免疫染色、3D成像、数据分析及存储
- 小动物活体成像
- 小动物近红外二区成像
- 纳米药物制备系统/服务
- 微流控纳米药物递送平台 纳米药物载体合成服务
- 超快超分辨功能超声成像系统
- 超快超分辨功能超声成像系统
- 活体多光子及高分辨显微成像系统
- 高分辨率显微成像系统 双光子荧光寿命计数系统 活体多光子显微成像系统
- 试剂耗材
- 抗体系列产品 GATTA 显微镜纳米标尺 RISystem小鼠骨钉 Cellendes细胞水凝胶
- 小动物灌注/灌流设备
- 小动物灌注系统 灌流设备及附件
- 类器官3D细胞培养
- 锘海类器官、3D细胞培养系统
- 生物3D打印设备
- RegenHU生物3D打印机
-
应用案例
- 成像视频
- 成像视频
- 成像图片
- 成像图片
- 新闻资讯
- 联系我们
当神经科学邂逅组织透明化——会演绎出怎样的故事?
发布日期:2022/2/10 10:03:36
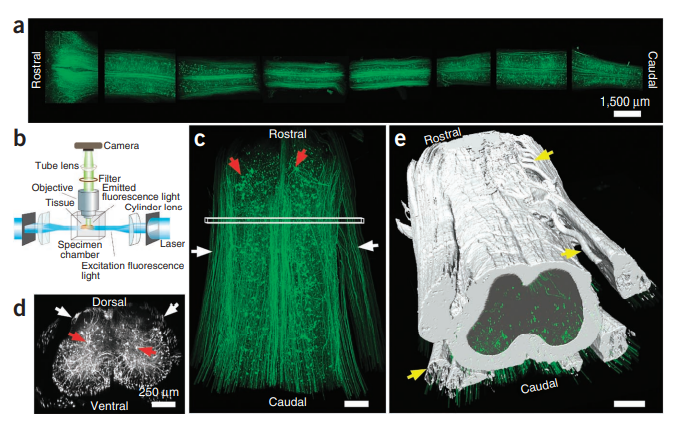
Imaging large regions of the spinal cord of GFP-M mice
(a) Entire spinal cord of a GFP-M mouse cut into 3- to 4-mm-long segments, cleared and imaged with ultramicroscopy. (b) Drawing of the ultramicroscopy setup showing tissue positioning and the light path. (c) A spinal cord segment (length 4 mm, T12 to L2 spine level) of a GFP-M mouse scanned with ultramicroscopy shown in a horizontal view. (d) Cross-view projection (50-μm thickness) of the indicated region in c. White arrows in c,d mark individual axons in the white matter; red arrows mark cell bodies in the gray matter. (e) Traced white and gray matter boundaries and axon bundles (yellow arrows).
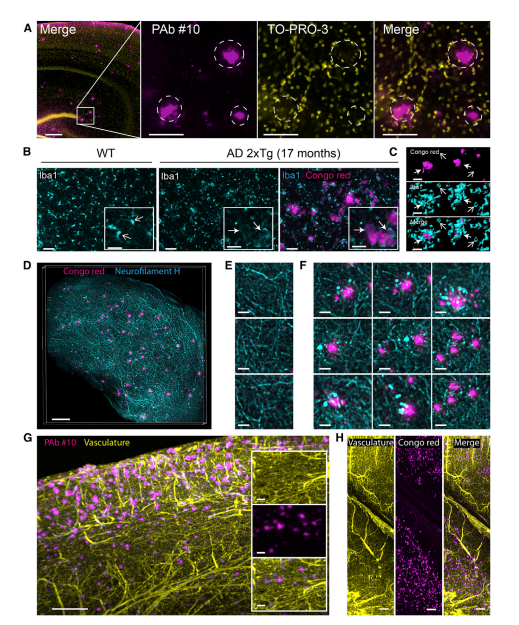
阿尔兹海默症(AD)是一种起病隐匿的进行性发展的神经系统退行性疾病。临床上以记忆障碍、失语、失用、失认、视空间技能损坏、执行功能障碍以及人格和行为改变等全面性痴呆表现为特征,细胞外β淀粉样蛋白沉积和细胞内tau蛋白磷酸化是AD的主要病理特征。Liebmann等人利用iDISCO技术对阿尔兹海默症模型小鼠脑进行透明化阐明了β淀粉样蛋白沉积和小胶质细胞及脉管系统之间的空间分布关系,这将对阿尔兹海默症的科学研究和治疗产生重大意义。
Chung等人通过CLARITY技术获得透明而完整的小鼠大脑,利用Thy1–eYFP信号实现了对小鼠大脑神经元进行远距离投射、神经回路、细胞关系、亚细胞结构、蛋白质复合物、 核酸和神经递质的成像。展现了大脑中复杂的精细连接和分子结构。
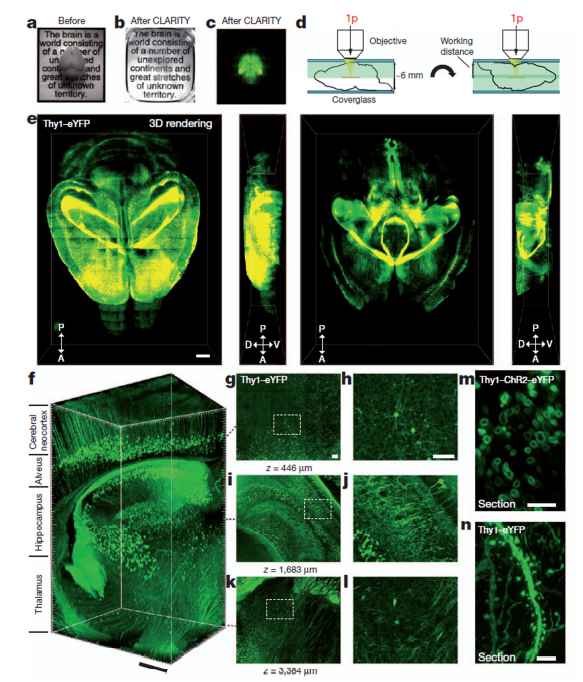
Intact adult mouse brain imaging
a, Cajal quote before CLARITY. b, Cajal quote after CLARITY: Thy1–eYFP line-H mouse brain after hydrogel–tissue hybridization, ETC and refractive-index matching. c, Fluorescence image of brain depicted in b. d, Dorsal aspect is imaged, then brain is inverted and ventral aspect imaged. e, Three-dimensional rendering of clarified brain imaged;f, Non sectioned mouse brain tissue showing cortex, hippocampus and thalamus;g–l, Optical sections from f showing negligible resolution;m, Cross-section of axons in clarified Thy1–channelrhodopsin2 (ChR2)–eYFP striatum;n, Dendrites and spines of neurons in clarified Thy1–eYFP line-H cortex.
MURAKAMI等人应用CUBIC-X透明并膨大小鼠大脑,在亚细胞水平对整个小鼠大脑进行成像,并绘制出了一张小鼠大脑图谱。他们采用化学方法标记了大脑中的每个细胞,然后在大脑透明化的同时将其尺寸扩大了十倍,利用精密成像技术对神经元进行了三维重建,总计约7200万个细胞。
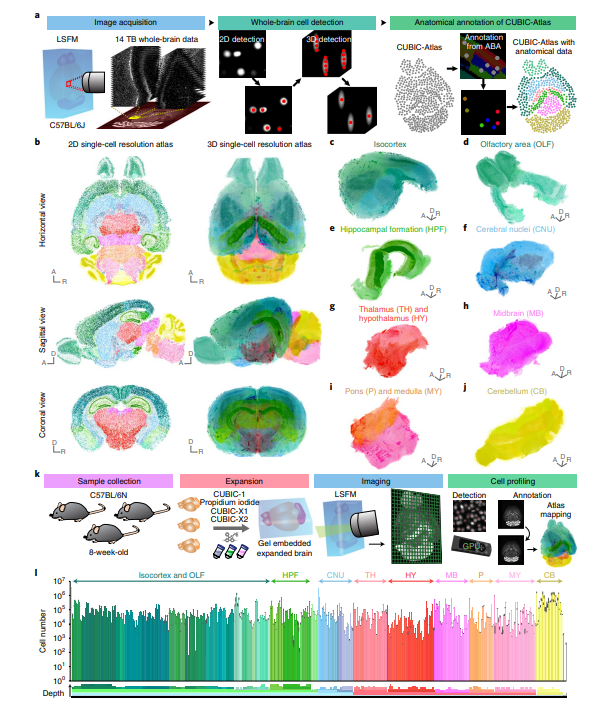
a, Overview of construction of the CUBIC-Atlas. b, The CUBIC-Atlas. Horizontal, sagittal and coronal view of single-plane images (left) and volume-rendered images (right) of the CUBIC-Atlas. c–j, Major anatomical areas in the CUBIC-Atlas. k, Overview of whole-brain cell counting in C57BL/6N 8-week-old male mice. l, Cell numbers in each brain area.
参考文献:

